By Sabz Ali.Mar 19, 2023
DevOps is a methodology that has become increasingly popular in recent years as organizations seek to improve their software delivery processes. DevOps emphasizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams, as well as automation and continuous integration and delivery. But what is DevOps culture, and how does it relate to software development lifecycles? In this article, we’ll explore the key elements of DevOps culture and the stages of software development lifecycles, as well as the differences between the Waterfall and Agile models. Whether you’re a software developer, operations engineer, or project manager, understanding DevOps culture and software development lifecycles can help you deliver high-quality software more efficiently and effectively.
What is DevOps
DevOps is a methodology that connects development team to the operations team for a continuous development and deployment of software basically The goal of DevOps is to create a culture of collaboration and communication between developers and operations teams, and to automate the software delivery process as much as possible. DevOps can help organizations improve their software quality, increase their agility, and reduce their time-to-market.
What is DevOps Culture
DevOps culture basically refers to shared responsibilities between operation team and development team for the products they create and maintain.
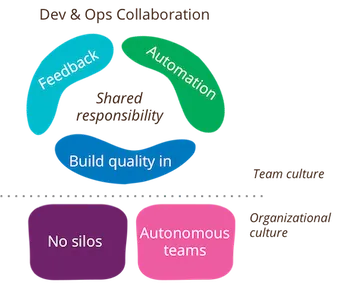
DevOps culture is characterized by the following elements:
- Collaboration: DevOps emphasizes the importance of collaboration and communication between development, operations, and other teams involved in the software delivery process.
- Automation: Automation is a key aspect of DevOps culture, as it allows teams to reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and increase efficiency.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery: DevOps promotes a continuous and iterative approach to software development and delivery, with frequent updates, testing, and deployment.
- Monitoring and Feedback: DevOps culture values continuous monitoring and feedback, in order to quickly detect and resolve issues and improve the software delivery process.
- Agile and Lean Principles: DevOps embraces agile and lean principles, which emphasize flexibility, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
To conclude, DevOps culture seeks to promote a more collaborative, efficient, and agile approach to software development and delivery, in order to meet the ever-changing needs of customers and stakeholders.
What are software development lifecycles(SDLC)
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a well-established process utilized by the software industry to design, develop, and test software applications to ensure they meet high-quality standards. The primary objective of SDLC is to create software that not only meets or surpasses customer expectations but is also completed within estimated timelines and budgetary constraints.
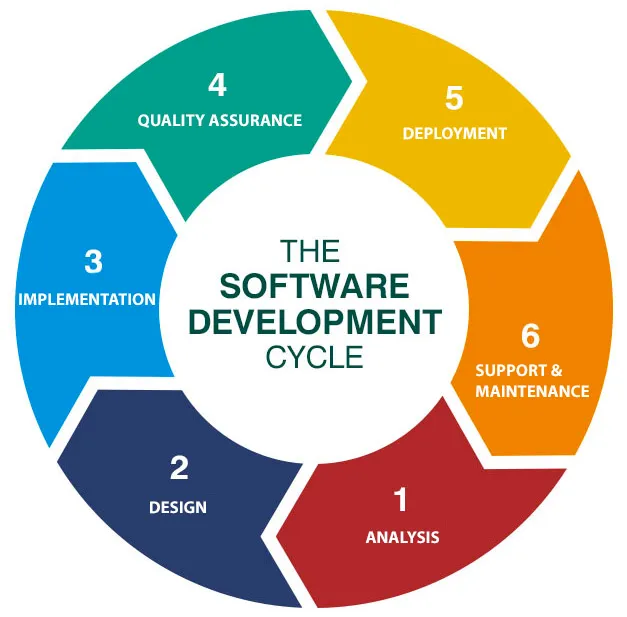
The process of software development involves multiple stages to ensure that the final product is of the highest quality and meets the needs of the users.
The first stage is requirements gathering and analysis, where the development team talks with stakeholders to understand their needs and gather the necessary requirements. During this stage, the team ensures that the requirements are clear, concise, and achievable.
The next stage is Design, where the team creates a detailed plan for the software application. This includes determining the software’s architecture, interface design, and data models.
Once the design is complete, the Development process begins in which the development team begins writing the code for the software application, following the coding standards and design specifications.
After the development stage the Testing phase begins, the software is tested thoroughly for bugs, defects, and errors. This includes a range of testing types, such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing.
If the software application passes the testing stage successfully, it’s then deployed to production, where it’s made available to the end-users and this phase is called Deployment phase.
Finally, the software application is monitored and maintained after deployment to ensure that it continues to function as expected. This includes fixing any bugs or errors that may arise, as well as providing updates and enhancements to improve the user experience this is the last phase of Software development life cycle and is called Maintenance phase.
There are several types of software development lifecycles, each with its own approach and set of stages. Some of the most commonly used software development lifecycles include:
- Waterfall Model
- Agile Model
Difference between Waterfall and Agile Model
The Waterfall model is a traditional software development approach that follows a linear and sequential process, where each phase of the development cycle is completed before the next phase begins. The approach is based on the assumption that the requirements and scope of the project are well-defined and stable. Waterfall follows a top-down approach, meaning the requirements are defined first, followed by design, development, testing, and finally, deployment.

However, the Waterfall model has some limitations. It is rigid and inflexible and does not allow for changes or revisions once a phase has been completed. This can lead to unforeseen problems and rework later in the project, which can result in increased costs and delays.
To overcome these limitations, a new approach to software development was needed, which gave birth to the Agile model. The Agile model is an iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and rapid development. Agile development cycles are shorter, and feedback from stakeholders is taken throughout the project, which helps in continuous improvement and course correction.
Agile development is based on a bottom-up approach, where the development team and stakeholders work together to identify and prioritize requirements, which are then broken down into smaller deliverables called sprints. Each sprint results in a working software increment that is tested, reviewed, and improved upon in the next sprint. Agile model allows for changes and modifications to be made at any stage of the development process based on the feedback received from stakeholders. This makes the Agile model more adaptable to changing requirements and ensures that the end product meets the customer’s needs.
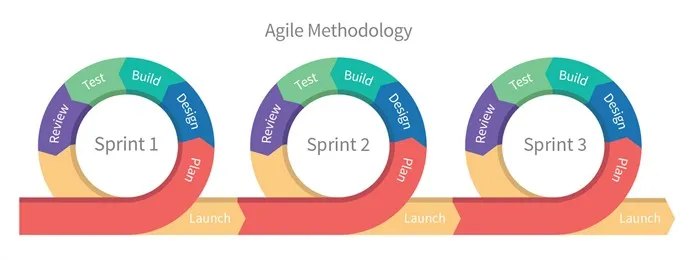
In summary, the Waterfall model is a linear and sequential approach, which is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and a fixed budget and timeline. On the other hand, Agile model is an iterative approach that emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and rapid development, which makes it more suitable for projects with rapidly changing requirements and a need for frequent feedback and collaboration.
In conclusion, DevOps culture promotes collaboration, automation, continuous integration and delivery, monitoring, and feedback. It seeks to improve the efficiency and agility of software development and delivery processes to meet the changing needs of customers and stakeholders. Meanwhile, the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides a well-established process for designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software applications. The Waterfall and Agile models are two popular SDLC approaches, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Ultimately, choosing the right SDLC approach depends on the project’s requirements, budget, and timeline. By combining DevOps culture with the appropriate SDLC approach, organizations can improve their software quality, increase their agility, and reduce their time-to-market.
The original article published on Medium.
